Category Archives: uncategorized

Panther Pest Control Blog
Keep your home pest-free with Panther Pest Control:
- Expert pest control services for homes and businesses.
- Safe, effective, and environmentally-friendly treatments.
- Trusted professionals dedicated to eliminating pests for good.
Nowadays, more and more people ramp up their efforts to establish an environment-conscious lifestyle. This significant step is of great importance to both health and environmental protection, as the use of varying chemicals for pest control, especially pesticides, is only getting worse, not to mention nature adapting.
Green-oriented people buy and consume organic food and bits – cleaners, cosmetics, clothes, etc., or create such themselves. Alongside organic products, they seek services that are ecological, too.
Amongst these services are green treatments for both your home and pest control for business. Appealing to the upward sustainable trend, it gains a lot of attention these days. That’s because conscious consumers prefer to avoid traditional pest treatments since they create health risks and contribute to environmental pollution. And green pest control eliminates pests with the lowest possible harmful impact on the surroundings.
So, you are part of this new wave of environmentalism and want to learn more about green pest management?
Read ahead to discover a detailed variety of organic pest control methods and products to handle troublemakers, put together by the team of experts at the Panther Pest Control Company.
In the pest management industry, there are a lot of similar terms related to ecological services. You hear about “green”, “natural”, “eco-friendly”, “chemical-free” pest control, and more. But none of them owns a well-defined explanation. So, it’s important that you learn the major differences to make a well-informed decision when you choose a service for your home or office.
Green/Chemical-free Pest Control
This type of pest management refers to products that come only from earth-based materials and contain non-chemical matters. Such natural materials are borates and desiccant dust (diatomaceous earth and silica).
Green pest control doesn’t exclude pesticides entirely. It’s a practice focused on the secure application of naturally occurring pesticides, because just as pests cause allergies, so could traditional pest treatments.
Botanical insecticides and pesticides are perfect examples. These substances kill pests on contact effectively. But mind that they lack residual effect. Thus green pesticides are not suitable for persistent pest troubles.
Environmentally Conscious Pest Control
This is another alternative of pest control with reduced harmful effects. But it doesn’t limit the use of synthetic products and non-natural pesticides.
However, they contain only low toxicity chemicals and reduced-risk materials. Plus, eco-friendly products usually come in handy for particular situations – to target a specific pest or treat a specific area.
Exterminators & Green Pest Control
There are progressive pest management companies that respond to the growing demands for eco-friendly services. How do they perform green control to combat rodents and insects?
Alongside with green and environmentally conscious products, detergent water, vacuum cleaners, and door sweeps are on the front lines of green pest control.
Compared to traditional exterminators who rely on strong and harmful pesticides, eco exterminators have a different approach.
- First, experts investigate how and why pests infiltrate a particular place.
- Then, professionals use the mentioned tools and natural products to eliminate the problem.
For example, door sweeps are great to fill gaps underneath doors and stop mice invasion. And a natural insecticide like Orange Guard suffocates insects. Products with earth-based materials like diatomaceous earth (mentioned above) destroy the insects’ protective shells to kill them for good.
The goal of eco-exterminators is the use of techniques and products detrimental to pests, but as low toxic as possible for you and the environment.
Now, Let’s Review Green Pest Control Methods
1. Companion Planting
This is a gardening method to control pests in your yard. It’s a technique in which plants protect other plants. Plant specific greenery near your existing plants to eliminate pests, maximise space, and also increase crop productivity.
Crops provide a habitat for insects that feed on bugs inhabiting the crops of your existing plants. That’s how you get rid of pests and save your plants.
Leeks work great to protect carrots. Lettuces planted near radishes repel flies from them thanks to a specific smell. Daffodils drive out mice, while onions – rabbits. And castor beans get you rid of moles.
Learn How To Protect Your Garden & Get Rid of Woodlice
2. Trap Crops
If you don’t need additional plants, there are trap crops to plant directly and attract unwanted pests from existing crops that you need. When you protect the wanted crops from bugs, you preserve them healthy to harvest.
Plant the trap crops around the perimeter of your garden and match the pests’ invasion period for best results.
3. Parasitic Nematodes
These microorganisms naturally thrive in the soil. Once inside an insect, they release bacteria which kill the pest in a day or two. Better still, the animal experts at All About Cats state, “Parasitic nematodes are safe around pets as well as plants and people.”
So, there is a pest control technique to increase the number of parasitic nematodes in the soil. This stimulates the elimination of the troublemakers.
Try Nematodes to fight armyworms, squash vine borers, soil-dwelling grubs, and roots maggots.
Green Pest Control Products
1. Floating Row Cover
This is a translucent, porous polyester fabric that acts as a barrier for pests. Cover your plants to protect them when they are most vulnerable, like when the pests are most active.
Row covers are useful to keep away mobile pests, such as cabbage moths, aphids, squash bugs, beetles, and tomato hornworms.
Combine row covers with trap crops to handle pests that overwinter in the soil.
2. Pheromone Traps
Many insects release a strong smell to lure the opposite sex.
There are special traps infused with such a scent to attract a target insect. Mind that they lure mostly male insects, so they are not quite effective. Also, when you notice a pest trapped in the bait, use other control strategies like the application of the row cover.
Pheromones lure is powerful towards moths, corn earworms, tomato pinworms, cutworms, etc.
3. Sticky Traps
These are tapes from a specific rigid material and texture, covered with a sticky matter. They are in a particular colour that attracts the target insect. Use at least several sticky traps and keep them clean for efficient results.
This safe pest control gear gets you rid of whiteflies, fruit flies, leafhoppers, cucumber beetles, flea beetles, and fungus gnats.
4. Insecticidal Soap
This product contains unsaturated fatty acids that dissolve the skin of insects, so they die. It’s best to use the soap while it’s liquid. Once it dries, it has no effects on the pests. So apply as a solution with a spray bottle.
The soap is effective against mites, whiteflies, and the softer nymph stages of some bugs.
5. Bacillus Thuringiensis
Another microorganism that naturally occurs in the soil. Once in a pest, these bacteria release a specific protein. This detrimental to pests protein makes them stop eating, and eventually, they die.
Buy a liquid containing Bacillus Thuringiensis (BT) or a powder of it to dilute with water. Spray the product directly on the plants you want to protect.
BT combats the diversity of caterpillars and Colorado potato beetles.
Essential Oils as Natural Pesticides
What’s a better way to let organic pest control in your home or office than the application of everyday natural products?
Essential oils are a simple, inexpensive, and effective approach for that.
- Peppermint, Eucalyptus. These work great for handling spiders, roaches, and flying bugs infestations. They cope with even bigger pests, too – beetles, caterpillars, moths, etc.
If you know where the bugs get in your house, place an undiluted line of these oils on the area. This is a certain trick to keep them out.
And what if you’re not sure how the pests enter? Then, prepare a mixture of 15 drops of oil and 12 ounces of water. Spray the solution to a wider area. Or spray cotton balls with the mixture and display them in crevices around the place.
- Lavender, Lemongrass. Use these essential oils before you reach out to professional exterminators of fleas, ticks, mosquitoes, and other insects that bite.
Again, make a mixture like the previous with any of these oils and apply it the same way.
Use it also to spray your pet’s coat once a week or add 2 drops of oil to their shampoo to prevent fleas on pets.
- Rosemary, Basil. Get these oils to repel flies and protect yourself and your close ones from the awful diseases they carry.
Put a sponge in a jar and drip it with several drops of oil. Place the jar near the affected area, so the oil scent drives the flies away.
- Spearmint, Lemon. These essential oils help get rid of ants. These tenacious bugs crawl everywhere there’s food.
Mix 15 drops of spearmint oil and 7 drops of lemon oil in a spray bottle. Saray your kitchen counters, cabinets, table, and fridge to eliminate ants and preserve your food.
Remarks On Green Pest Control
Whether you perform it yourself or hire a pest control company to do it, green pest control exists and is worth a try.
Pests are, without a doubt, a serious problem that deserves a responsible solution. But rather than strong, harmful synthetic chemicals, consider using natural products and methods to get rid of creatures, causing trouble in your life.

Panther Pest Control Blog
Keep your home pest-free with Panther Pest Control:
- Expert pest control services for homes and businesses.
- Safe, effective, and environmentally-friendly treatments.
- Trusted professionals dedicated to eliminating pests for good.
This chapter is about bird control methods. Should you or shouldn’t you use chemical pest control means to get rid of the vermin? It can be tricky because some types of birds are beneficial to your garden, and you have to make sure that you use the right methods to only keep the annoying birds away.
Bird Control Methods
In the United Kingdom some bird species are considered as pests. If you ask anyone who’ve had birds landing, roosting and nesting in their business property, he will be glad to hear that there are plenty of methods to eliminate or deter these nuisance pests.
In large numbers birds can be responsible for variety of problems to your business such as pigeon diseases spread through their feces, including histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, and psittacosis. It’s really important to take measures on time, otherwise some damage to property and equipment may also occur.
Another problem that farmers may face is birds attacking their crops and fruit orchards. Several bird control methods may solve this problem. The most effective ones are generally a combination of a few pest control techniques.
Which bird species are seen as pests in the UK
- Black-backed gull;
- Lesser black-backed gull;
- Herring gull;
- Feral pigeon;
- Starling;
- Collared dove.
Bird Control Devices
Bird scarers

A bird scarer is any of a number devices designed to scare birds. Mostly employed by farmers on their crops to scare birds away from recently planted arable crops and dissuade them from eating the crops.
Another place where the scarers are frequently used on are the airfields, in order to prevent birds from accumulating near runways and causing a potential hazard to aircraft. There are two types of bird scarers which can be used – visual scarers and auditory scarers.
Scarecrow
Scarecrows are usually built from straw and wood and are one of the oldest designs knows for bird scarers. In medieval Britain, scarecrows were young boys who were tasked with the duty of scaring birds away. Their responsibility was to patrol wheat fields and keep any crow or starling that tried to land in the fields by running against them while screaming and throwing stones at the same time.
Scarecrows are mainly designed in the shape of a human figure, however not all visual scare devices are shaped like humans. This method doesn’t work so well with all species, considering that some species frequently perch on scarecrows.
Hawk kite
In natural some bird species are afraid of predators such as birds of prey. This is why the “Hawk kites” were designed. They fly from poles in the wind and protect the field by hovering above it. To design the perfect “Hawk kite” its shape should match exactly the silhouette of a bird of prey.
Helikites

A Helikite is a lighter-than-air combination of a kite and a disposable helium-filled balloon. It is frequently as an extremely effective solution for scaring birds. At the beginning, it was used only when windy, however, farmers and scientists needed something that would also fly in no wind.
Today there are two different types of bird scaring Helikites available. The Vigilante Helikite for temperate climates and the Lightweight Helikite for hot climates and tree fruit. They can fly up to 200 ft. in the air no matter if there is wind or not. Helikites can cover large areas of farmland and hover in the sky behaving like birds of prey.
Lasers
There is some evidence about some birds being laser-resistant, however, the use of lasers is still an effective method in order to keep pest birds away from the crops. Although some lasers prove to be effective during daylight hours, the most effective time to use them is at dawn and dusk because when the light levels are increasing the effectiveness of the laser decreases.
When using this method of bird control, the strong contrast between the ambient light and the laser beam startles the pest birds. This technique is very selective during low light conditions and can be attuned to frequencies and wavelengths that particular bird species don’t like. Things are different during night time because the light beam is visible over a large distance and can cause widespread disturbance. Due to safety regulations in some nations lasers above a certain power of the beam are prohibited by a law.
Dead birds

Birds have a specific behaviour towards dead animal species of the same kind. Birds even hold funeral through which they warn other birds of a nearby threat.. In addition to this, carcasses of birds are known to serve as a warning to other birds that deters them from the area where dead birds may be spotted.
This visual scarer relies on a model or an actual carcass used to signal danger to others. Pest birds often approach the dead body but usually leave when they see the unnatural position of the dead bird. This type of a scarer is often used in attempts to deter gulls from airports.
In case you have dead birds or other animals at your property, we are able to provide a dead animal removal service. Simply call us for more details how we do the service and what animals may be disposed by us.
Balloons

This is an inexpensive method which relies on the movement of balloons with which the birds get used to. People using this type of a scarer draw an additional illustration of an eye on the balloons because it has shown to increase the effectiveness of this method as it combats the birds’ ability to adapt.
There are also commercially available balloons. They all have holographic eyes from which the pest birds can’t hide because they follow them wherever they go. When the ”scare-eye” balloon placement is being moved periodically, the effectiveness of this method increases.
In the United Kingdom the use of balloons is subject to approval from the Civil Aviation Authority, especially around airfields.
Pyrotechnics
Fireworks and other kind of pyrotechnics have proved to be effective in dispersing birds at airports, landfill sites, agricultural crops and aquaculture facilities. The most common method of bird control by using pyrotechnics that is used in the United Kingdom is shellcrackers fired from a modified pistol.
It’s mostly used at airports and what makes it the best choice is the option that allows the bird controller to have some directional control over birds in flight, so they can be steered away from runways. However, there is a risk of birds becoming used to pyrotechnics or cartridge explosions.
Radio-controlled aircraft
One of the primary bird harassment methods used to keep airfields safe and clear of raptors and other large birds is the radio controlled aircraft. This type of a scarer have been used since the early 80s to haze pest birds mainly over airfields, agricultural areas and landfill sites. It has been recorded that birds habituate slowly to a treatment in which they are being actively hazed and this is why RC aircraft has been shown to be very effective against bird infestations.
Bird Control Spikes

Installing bird control spikes, usually on the roof of a property, is a bird control method we offer as part of our bird control and prevention services.
The bird control spike, also known as an anti-roosting spike or roost modification, is an effective and humane solution against larger bird infestations. The device consists of long, needle-like rods and there are two types of spikes available – in plastic and stainless steel.
Bird control spikes can prevent wild and feral birds from perching or roosting at public spaces this is why they can be easily attached to building ledges, street lighting, and commercial signage. Some pest birds produce lots of unsightly and unhygienic feces, other can be inconvenient for neighbours by making strange and loud noises, especially at night.
This is why bird control spike are coming to the rescue without causing harm or killing the birds. The birds get a slightly stabb and stay unharmed. The RSPB (Royal Society for the Protection of Birds) recommends bird control spikes for deterring pigeons from gardens.
If left unchecked, the spikes are getting clogged by leaves, debris and feathers which allows the pest birds to perch easily on top. In addition, this bird control method can make some landmark buildings look less attractive or untidy. In these cases, it would be better to implement other methods of bird control such as barriers that do not allow the birds to be in an area or on a surface.
Barriers will totally exclude netting and mesh from unwanted areas. The low current electric won’t allow nesting, roosting, or loafing birds at any surface. Spikes attract small birds or pigeons which nest right into the spikes by providing large amounts of nesting debris, twigs, and grass as well. This is why it’s much more preferable to start with netting and low current barriers because these methods have proven to be effective each time they were used.
Bird netting
Birds damaging vegetable and fruit crops as well as seedlings are considered as pests. Farmers don’t like it because when birds start pecking one fruit, they continue to another one. Therefore to prevent great damages bird nets are used. If even a small portion of the fruit is bitten off, it cannot be harvested and sold respectively, because it will go into rot or fermentation damaging the rest of the harvested case.
Places where you can apply bird netting protection:
- Directly on stand-alone trees;
- Espaliers – peaches, pears, apples, grapes;
- Berries – strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, cranberries;
- On the side ventilation windows of growing tunnels;
Fish protection
Fish farmers are forced to rely on bird netting in order to protect fisheries, stocked ponds or their shrimp and tilapia breeding-pools from predatory birds. These nets are usually white, so they can be easily noticed by the large birds, which will prevent them from diving into the water for their next meal. The nets have larger mesh size and in order to make them more resistant individual strands are used for their construction, because fish farmers tend to install them on cable systems crossing the whole expanse of the water surface.
Mining Ponds
Mining ponds are extremely dangerous and potentially life threatening for the wildlife, therefore the US EPA has demanded that these cyanide rich ponds must be covered at all times. The hazardous chemical elements, used in the process of extracting minerals and metals from crushed rocks, must be confined from easily spreading in the environment.
Bird trapping
There are various techniques for capturing wild birds. The primary purpose of these trapping techniques was hunting birds for food but nowadays that is no longer the case. At the present time, birds can be captured for use in ornithology research or to be kept as pets. They can also be trapped for display in zoo gardens and all that contemporary use of birds requires that they are not harmed when being trapped. In order to preserve the bird’s population and diversity, many countries have strict laws and regulations towards capturing wild birds.
Clap traps

A claptrap is a device made to catch and trap birds. It consists of two parts that are made of the net with wooden or metallic frames and are kept in a furled position. When a bird gets into the trap, the movement triggers the springs attached to the frames and the two halves close in on each other, trapping the bird between them.
This device is usually used for birds that tend to perch on easily accessible places or on a still water, where would be easy for people to check on the trap regularly. Clap traps can be placed on a location with high concentration of birds or it’s possible to use luring devices to draw in the birds to it.
Funnel traps / Corral traps
Some bird traps are built to have an entrance in the form of a funnel (hence the name “funnel traps”). This narrow entrance is used to drive the birds into a wide, large corral that gives the other name for these traps. A much larger version of this trap is named “Heligoland trap” after the German bird observatory at Heligoland where it was first designed.
Mist nets

Mist nets are thin nets convenient for catching wild birds. The invisible net is tightening across the trees in a way that it hinders the flight path of a bird. It flies into the mist net and gets entrapped in it. The nets are often used in bird ringing and are generally never left without supervision. A single bird that captures in the mist net is immediately removed. This is required in order not to injure the bird and to prevent it from being killed.

Panther Pest Control Blog
Keep your home pest-free with Panther Pest Control:
- Expert pest control services for homes and businesses.
- Safe, effective, and environmentally-friendly treatments.
- Trusted professionals dedicated to eliminating pests for good.
Finally, we’ve managed to get all bed bugs facts and myths in one place. This guide will get even bigger over time and we will try to cover any information related to bed bugs that are either a fact or a myth?
General Facts & Myths About Bed Bugs
Bed Bug Myth #1 – Bed Bug Are Most Active at Night?
True. Bed bugs usually crawl out under your mattress and will attack you in your sleep when it’s dark. However, the nasty insects would feed during the day as well if they feel safe.
Bed Bug Myth #2 – Eggs and shed skins are a sign of bed bug infestation?
Mostly False. Bed bug’s eggs are distinctive but it’s still possible to not recognize them or mistake them with those of other insects. Skin sheds are easier to define but only if they are whole. The only true sign that there is a bed bug infestation is seeing living bed bugs.
Bed Bug Myth #3 – Bed bugs live in clothes?!
Very true. Bed bugs will get inside your clothes because this is the way they move long distances. It’s also the main reason for domestic infestations – people coming back from trips bring bed bugs at their home along with the luggage.
Bed Bug Myth #4 – The Bugs May Leave Dark Spots on Your Sheets?
True. Usually, these are faecal traces. Bed bugs may leave such marks anywhere in the room but especially on the sheets. After all, they feed quite often and multiply very fast.
Bed Bug Myth #5 – Bed Bugs Can Survive a Whole Year Without Food
False mostly. This is a very popular bed bug myth you’ll see anywhere on the web. The truth is, a bed bug is able to survive that long only if its adult and spends the whole 1 year at a temperature of 10 °C, which is kind of impossible. In a room with the most favourable temperature for the insects, bed bugs will survive for only 100 days without food.
Bed Bug Myth #6 – It’s a Good Idea to Throw a Mattress if it’s Infested?

False. Some would suggest getting rid of your mattress just because it cannot be treated with insecticides. That’s not true, you can use heat treatment to kill the bed bugs or you can follow these tips on how to treat bed bugs on mattress.
Bed Bug Myth #7 – Bed Bugs are Scared of Light!?
Not true. Bed bugs will come out and bite you even when the lights are turned on. The heat and carbon dioxide our bodies emit during sleep is very attractive to the insects, lightness will not scare them, especially if the bugs are hungry.
Bed Bug Myth #8 – Vacuuming and Decluttering Helps to Avoid Bed Bug Infestation
True. Mostly because bed bugs use the clutter as hiding spots, which makes the identification and extermination harder. If clutter is minimized, you will take precautions to exterminate them earlier or might even spot the bed bug before it reproduces.
Bed Bug Myth #9 – Bed Bugs Live Only in Big Cities.
Wrong. According to the “Bed Bugs in America” survey done by NPMA, the creatures were spotted in all 50 states of the country. In the UK, they are present everywhere but mostly in London.
Bed Bug Myth #10 – Bed Bugs Can Survive at -50°C.
Nope. At this temperature, the species dies pretty fast. According to Science News, this has been tried already. Scientists have already experimented on bed bugs and low temperatures. It was found that the lowest temperature was -25°C at which only an egg would survive but not an adult bug.
Bed Bug Myth #11 – Bed Bugs Have Wings and Fly.
Hilarious. This is not true at all. Still, there are many people who ask “Can bed bugs fly?”. Bed bugs are unable to fly, they can’t even jump (this is what ticks do). The only way for bed bugs to move is by crawling. They still have wings, also known as hemlytral pads but there are no hind wins.
Bed Bug Myth #12 – You Can Find Bed Bugs in Kitchen Appliances?!
True. As we’ve already mentioned, bed bugs are attracted by darkness and heat, an oven that’s been recently turned off is such a thing. Don’t be stressed if you spot a bed bug crawling out of a kitchen appliance, try to identify if it’s really a bed bug instead.
Bed Bug Myth #13 – Keeping The Suitcase Away Helps?
Very true. It’s even highly recommended when you spend a night at a hotel to keep your luggage away from the floor and the bed. Use a rack or the top of the wardrobe – these are harder for bed bugs to reach.
Fact #1 – Bed Bugs Can Live Anywhere In Your Home. Not Just in the Mattress.
There aren’t multiple opinions on this, so it’s more like a fact. Bed bugs may live in any place that is dark and provides a form of shelter. That would be inside cracks in the walls or furniture and in your luggage no matter if it’s packed or not.
Bed Bug Fact #2 – Adults may reach a size of over 7mm in length.
That would be kinda hard but it’s not impossible. Usually, an adult bed bug’s size is about 6mm but when fed up with blood it’s possible to grow even further. The usual maximum length though is about 5-6mm. Read more about how big are bed bugs to learn anything about the size of bed bugs (bed bug pictures included).
Bed Bug Fact #3 – The most favourable temperatures for bed bugs are 70-80F (21 – 26 °C).
Bed bugs will reproduce best at this temperature. It’s also important to know that a temperature of 56°C (132F) or more will kill a bed bug at any life stage. This is the exact temperature at which a room is heated during a bed bug heat treatment, which is one of the most effective ways of bed bugs extermination.
Bed Bug Fact #4 – Bed Bugs Are Predictable.
That’s true only when it comes to their feeding habits. A typical bed bug would prefer not to spend more than 10 minutes on its victim. Another typical feature is that this insect would live as near as possible to the victim. That’s why bed bugs usually live under the mattress – it’s simply very close to the sleeping person.
Bed Bug Fact #5 – An Adult Female Bed bug Lays About 200-500 Eggs.
A female bed bug is able to lay 1-5 eggs a day which is about 200-500 during its whole lifetime. Their lifespan is a very important factor that makes this possible. A single bug lives about 300 days at the most favourable conditions.
Bed Bug Fact #6 – They Can Travel Up to 30 Meters to Take a Bite.
Although bed bugs prefer to live nearby their victims, when this isn’t possible, the creatures show severe persistence and go the extra mile in seek of some fresh blood.
Bed Bug Fact #7 – They Go Through Metamorphosis
We’re have explained carefully all stages of the bed bugs in our post about the size of bed bugs. But yes, a bed bug would go through many stages, most of which require a blood meal to finish successfully.
Bed Bug Fact #8 – Males Have a Bigger Abdomen.
This is a working trick that may help you find out if a bed bug is male or female. Males have much more edgy abdomen.
Facts & Myths About Bed Bug Bites

Bed Bug Fact #9 – Bites From Bed Bugs Are Painless
This is a fact and most people won’t react at all from the bite. The reason for this is the bed bug’s saliva. It contains anaesthetic substances and increases the blood flow at the bitten place. Next time when you wake up bitten by bed bugs, don’t wonder why you haven’t wakened up.
Bed Bug Myth #14 – Bed Bug Bites Are not Dangerous
Generally, this is true. You don’t even need a treatment after being bitten but if the rash is too painful you can seek medical help. The only concerning thing about bed bug bites is developing an allergic reaction. If this happens, avoid scratching.
Bed Bug Myth #15 – Bed Bug Bites Are Hard to Distinguish.
Quite true. Mostly, bed bug bites are confused with a tick, fleas or mosquito bites. There’s no way to easily find out if it was a bed bug that bit you.
Bed Bug Facts & Myths About Treatments

Bed Bug Myth #15 – Bed Bugs Are Evolving a Resistancy?
Very true. According to a study by the Scientific Reports, pyrethroid is one of the organic compounds to which bed bugs are now more resistant. We suggest reading their whole extensive case study if you’re interested in learning more about the evolution of bed bugs.
Bed Bug Myth #16 – Bed Bugs Die at 50°C
Debatable. This is a very high temperature for the bed bug and it will certainly not feel comfortable at it. A long exposure will finish it but we heat premises up to 56°C to make sure the insect will be exterminated at any phase. This can be done safely by bed bugs control specialists.
Bed Bug Myth #17 – Repeated Bed Bug Treatments Are Often Required.
That’s true, unless you do a professional heat treatment from the start. If pesticides are used, one treatment might not be enough. Some people do the mistake to clean the surfaces that have just been treated with pesticides. A professional pest control company will inform you of the proper post-treatment instructions.
Bed Bug Myth #18 – Drying Agents Kill Bed Bugs
Yes, in most cases. Drying agents a.k.a. desiccants are usually an effective substance for bed bug treatments. Use desiccants that are labeled as pesticides, otherwise you are risking to get your time wasted.

Panther Pest Control Blog
Keep your home pest-free with Panther Pest Control:
- Expert pest control services for homes and businesses.
- Safe, effective, and environmentally-friendly treatments.
- Trusted professionals dedicated to eliminating pests for good.
You must have seen different spiders in your house, but do you know their names? There are over 600 species of spiders in the UK and you may have encountered most of them one way or another. Some species prefer to live outside in nature, while others find your home to be the perfect place to live. Here are some of the most common spiders you would find in your British home.
False Widow Spider

Name: Steatoda nobilis, or also known as noble false widow and referred to as the false widow.
Appearance: Body length without legs of adult female is between 6-11 mm, while in males it ranges from 4-9 mm. The brown bulbous abdomen is with a cream-coloured marking which is often compared to the shape of a skull. Legs are reddish-orange.
Life Span: Females can live up to six years, while as per usual – males don’t live long after mating. His total life span is about 12 to 18 months total.
Habitat: Native to Madeira and the Canary Islands from where it allegedly spread to Europe. Arrived in England before 1879, perhaps through cargo ships. From its origin, we understand this spider usually prefers southern climates and warmer settings, nonetheless, its range appears to be expanding northwards.
Danger Level: In England this is one of the few local spider species which is known to cause pain to humans via its bite. However, symptoms of these bites are mostly similar to a bee or wasp sting, without any long-term effect.
Giant House Spider
Name: Eratigena atrica
Appearance: The giant house spider is between 12 – 18mm in length, with the females being bigger. Generally dark brown in colour with earthy tones of light brown and yellow or muddy red. What stands out is their hairy abdomen, palps and legs.
Life Span: The average life of the male spider was 33.9 days and 116.5 days for the female.
Habitat: Originally from north western Europe, this spider used to live mostly in caves or under rocks in dry forests, but today is a common spider in people’s households.
Danger Level: Harmless to humans or pets, further more this spider would rather escape than head on to battle.
Domestic House Spider

Name: Tegenaria domestica, as known as the barn funnel weaver in North America and the domestic house spider in Europe.
Appearance: Females are about 8 to 12 mm in size, while males are slightly smaller between 6-9 mm. Their body is elongated, with a flattened and straight abdomen. Body to legs ratio is typically about 50-60%. They are typically dark orange to brown or beige greyish, with a usual characteristic of striped legs and two dull, black stripes along the length of the cephalothorax.
Life Span: Indoor females usually live for over one or two years on the same web, while some may survive as long as seven years in rarely disturbed places. Outdoor females die when cold weather sets, while males rarely live for over a year.
Habitat: Domestic house spiders range worldwide from as north as Sweden to as south as Greece in Europe. Some also inhabit parts of Western Asia. They can survive longer in undisturbed sheltered places such as attics, basement or cellar parts, storage rooms, etc.
Danger Level: T. domestica rarely bite, if they do – it is painless. They are not aggressive at all and usually retreat when confronted. It’s easy to remove these spiders without killing them, as they are usually cooperative.
Daddy Long Legs Spider

Name: Pholcidae, commonly known as cellar spiders.
Appearance: Fragile arachnids, 2–10 mm in length with legs which may be up to 50 mm long. Often mistaken with the harvestmen (Opiliones) or crane flies.
Life Span: Around six and a half months.
Habitat: Pholcids can be found in every continent in the world, except Antarctica of course, where it’s far too cold for them to survive. These spiders hang inverted in messy, tangled webs constructed in dark and damp spaces. Such as caves, under rocks and loose bark, inside abandoned mammal burrows and undisturbed areas in buildings, such as cellars. Pholcids are also commonly found in warm, dry places such as household windows and attics.
Danger Level: There are far too many misconceptions surrounding the Daddy long legs spiders. All misconceptions aside – these spiders are harmless. Their fangs are too small to puncture human skin. Also, they probably would not attempt to bite at all.
Cupboard Spider

Name: Steatoda grossa
Appearance: Similarly to the black widows, the females are 6-10.5mm in length, dark coloured with a round bulbous abdomen. Their colouration ranges from purplish-brown to black with light-coloured markings. Unlike black widows and other species, the cupboard spider doesn’t have a bright pattern or other bright markings.
Life Span: Females can live up to six years, while the typical lifespan for the male is about one – one and half years. This is due to the fact that males often die shortly after mating.
Habitat: Found in many parts of the world, including all three coasts of North America, in Australia, New Zealand and in Europe. They can go several months without food, but only if they have access to water. These spiders construct cobwebs and as other web-weavers, they have poor eyesight depending mostly on vibrations coming through their webs.
Danger Level: Medically significant in humans, but minor with no long-term effects. Intrusions by large creatures will cause these spiders to flee, hence they are not aggressive. That being said most injuries to humans are defensive bites or honest mistakes. Symptoms of cupboard spiders are general malaise for a couple of days which may include blistering where the bite is, muscle spasms, pain, fever and sweating.
Hopefully, you can distinguish them now and know which ones to be especially careful about. If you notice a spider infestation you cannot deal with on your own, call Panther Pest Control and a spider exterminator will be at your door right away!

Panther Pest Control Blog
Keep your home pest-free with Panther Pest Control:
- Expert pest control services for homes and businesses.
- Safe, effective, and environmentally-friendly treatments.
- Trusted professionals dedicated to eliminating pests for good.
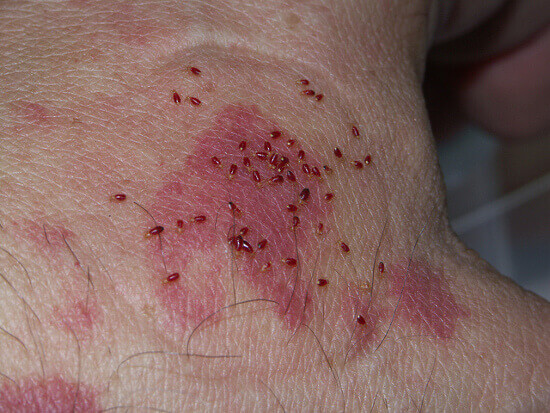
Woodlice may look like insects, but in fact, they are fourteen-legged crustaceans related to lobsters. Unlike their relatives, however, they have adapted to living on land. Still, woodlice need a damp conditions to be able to survive. It’s thought there are about 3,500 species of woodlice in the world and about 35-40 of these can be found solely on the British Isles. Some species such as the common sea slater are only found on the coast. Woodlice are a common pest nuisance in humid climates and damp conditions, mostly in gardens and wooden structures.
Woodlice Identification
It’s pretty easy to identify a woodlice problem, as they have very specific characteristics. The problem is catching a glimpse of them, as they are active mainly at night. A woodlouse has an outer shell called an exoskeleton, which it must shed as it grows. The moult happens in two stages, unlike that of most arthropods which are shed all at once. The first back half of the shell is shed and a day or so later the front half falls off. Woodlice also have a pair of antennae to help them find their way around and two small ‘tubes’, called uropods on the back of their bodies which help them to navigate. Also, some species use these tubes to produce chemicals which discourage predators.
Quick Woodlice Fact Sheet
- Woodlice are also commonly known as pill bugs, roly-poly and slaters. “Pill bug” and “roly-poly” because of its ability to roll into a ball.
- The pill bugs absorb water from the air, which makes humidity a key condition for their habitat;
- Woodlice are mainly detritivores, feeding off dead plant matter, fungi and their own faeces, but sometimes they may attack seedlings;
- Usually nocturnal animals, hence they are most active at night;
- Rolly pollies breed in the summer;
- Females can breed asexually, resulting in up to 200 young woodlice that live up to four years;
- Woodlice choose to hide in the moist, dark areas in your garden, such as under the mulch, compost heap, rotting timber, rocks, bricks, weeds, even in walls;
- Apart from man, its main natural enemies are spiders, centipedes, wasps, toads and shrews.
- Woodlice presence inside a property may indicate a dampness problem;
Plants Preferred by Woodlice
Although the woodlice diet usually consists of fallen leaves, sticks and other plant debris, in large woodlice populations attack to these plants may be exhibited:
- Ripe strawberries;
- Seedlings;
- Other fallen fruits;
What Can You Do to Minimize the Chances of Woodlice Infestation?
Generally, woodlice are considered beneficial in gardens as they produce compost and overturn the soil, but in large numbers (or infestation) and lack of food sources they are known to turn to cultivated plants, such as ripening strawberries and seedlings. On some occasions, woodlice may be spotted infesting homes in search of moisture, in which case their presence can indicate dampness problems that need to be addressed as soon as possible. Either way, pill bugs are not regarded as a serious household nuisance as they do not spread disease or damage wood. Nonetheless, woodlice can be a nuisance especially to gardeners and home-owners and happily there is a way to minimize the chances of pest infestation:
- Optimize your composting heap – better heating will reduce the moisture level thus avoiding the needed environment for woodlice habitat;
- Watch the water – be careful not to over-water your plants and avoid leaving other water sources that might aid a humid setting;
- Move the mulch – keep mulch away from the garden and especially seedlings;
- Biological control – pill bugs have natural enemies aplenty (some praying exclusively on woodlice) such as the woodlouse spider Dysdera crocata;
- Woodlice trap – pieces of cut potato, orange peels, strawberries and grated cheese, wrapped up in a damp newspaper. Put the bait in a damp area of your garden and leave it until woodlice come to infest it. After they do, just collect the trap and dispose of it.
- Keep the place tidy – remove any rotting timber, rocks, bricks, compost, weeds, mulch or other objects that are not needed;
We hope that this information will help you keep your garden pest-free and your plants beautiful as ever. If you have any further questions or need help with your pest problem, don’t hesitate to ask us for advice or assistance.
Techniques and Home Remedies for Preventing Woodlice Infestations
- Clean your gutters. Not maintaining them often causes woodlice infestation.
- Remove mold anywhere around the property
- Use electrical pest repellents.
- Minimize moisture – it’s essential for the pest’s survival.
- Fill tiny crevices where woodlice may hide (under stones in the garden)
- Remove food not stored in plastic or metal containers and get rid of any food waste such as compost bins.
If any of the ideas suggested above prove to be inefficient, don’t hesitate to seek professional help from Panther Pest Control. Call us at any time and get rid of the woodlice in your garden once and for all.

Panther Pest Control Blog
Keep your home pest-free with Panther Pest Control:
- Expert pest control services for homes and businesses.
- Safe, effective, and environmentally-friendly treatments.
- Trusted professionals dedicated to eliminating pests for good.
After the detailed guide on biological pest control in the previous chapter, it’s now time to present you anything you need to know about the chemical pest control methods used for pest extermination anywhere across the world.
They are not so sustainable as the organic ones but are often more effective and will be used in future even more extensively. You need to be familiar with the most popular chemical pesticides and their effect on production and the environment because it’s strictly related to your health.
Chemical pest control methods
Chemical pest control methods have been used for thousands of years by civilizations which had much less knowledge than the current population. Sumerians found out that sulfur gives great results in insect extermination.
However, the actual revolution in chemical pesticides happened during the 18th and 19th century when the industrial revolution required much more efficient pest treatments in terms of scale, effectiveness and speed.
To present days, chemical pest control methods are among the major types of vermin extermination practices and despite the fact that pesticides often lead to serious health issues, chemical compounds are vastly produced and sold across the whole world.
Here are the major types of chemical pesticides that are used nowadays in agriculture, domestic and commercial properties for pest control of various insects and rodents:
Fungicides

Fungicides are chemical compounds or organic organisms with biocidal properties, which help for the destruction of fungi and fungal spores. Fungi may cause severe disruption of any agricultural process.
This leads to losses of yield and lowers the final quality of the production. Apart from using fungicides in agriculture, they give very good results when used to cure fungal infections inside animals.
The major active ingredient of almost any fungicide is sulfur, which may turn out to be 0.5% of what is contained inside some of the heavier fungicides.
Here is the full list of fungicides used in agriculture. Refer to it whenever you need additional information
Advantages of Fungicides
- Fungicides control mycotoxin-producing pathogens
- Great value per cost. An artichoke production company in california earned 27 million pounds of artichokes for 1 000 pounds of chemical fungicide being invested.
- Kills fungi and fungal spores with great efficiency
List of Natural Fungicides
Fungi can be controlled effectively without the use of chemicals. It’s much more sustainable and causes no damage to the soil or pollution of any kind. Some plants do great job in the fight with fungi because of their naturally evolved defensive system.
Processing plants into sprays, mixtures and compounds of any other kind, turns out to be a great way to make natural fungicide. You can use any of the following extracts for the preparation of natural fungicides:
- Nimbin
- Tea tree oil
- Citronella oil
- Jojoba oil
- Rosemary oil
- Monocerin
- Oregano Oil
If you’re interested into making a fungicide yourself and buying any from the store sounds like a bad idea, don’t hesitate to take a look at this detailed on how to make DIY fungicide for plants.
Insecticides

Insecticides are any chemical substances that are used for insect extermination. They successfully help to eliminate insects and any life stage, including ovicides, larvicides, eggs and larvae.
Particular types of insecticides are used for exact purposes in a field like agriculture and medicine. One of the main reasons for the increased productivity of agriculture in the last century is the development of better and more affordable insecticides.
On the other hand, insecticides are able to cause damage to the ecosystem and health, that’s why recent studies and efforts are made towards increased implementation of organic pest control methods.
There two major classifications of insecticides:
- With residual effect
- Without residual effect (contact insecticides)
Another classification of the insecticides may be made based on their repellant qualities, this categorizes them in:
Repellent insecticides are more suitable when a pest is targeted for extermination. This way it will bring much of the insecticide to the colony and will wipe it out.
Repellents are used in agriculture when people want only to keep the pest away from plants. When extermination is not planned, repellents give great efficiency. The drawback is that repellents should be applied more often, especially if water has been applied over the plants after a rain for instance.
Repellents have much quicker effect in terms of crops preservation but don’t deal with the source of the infestation, while non-repellent insecticides kill the insect but such compounds are often more toxic and contaminate both – the soil and the crops often beyond the suggested requirements.
Synthetic insecticides
- Organophosphates and carbamates
- Neonicotinoids
- Ryanoids
- Organochlorides
- Pyrethroids (*should not be mistaken with pyrethrin, which is an organic compound)
Nematicides

Nematicide is a chemical pesticide which kills nematodes that parasitize on plants. The use of this chemical pesticide is very important for potato crops because of the soil-borne nematodes. Of course, nematicides may be natural such as extracts of neem oil.
Non-fumigant nematicides are among the most popular type. They have low volatility and spread easily after sprayed on soil. If water is sprayed on the soil the spreading of the non-fumigant nematicides becomes much faster.
In case the nematicides are naular, you can enhance their effect by manually inserting them deeper in the soil. A rainfall would also help but if the insecticide has been sprayed as a liquid.
Non-fumigant Nematicides
Non-fumigant nematicides have low volatility and diffuse through the soil (generally for short distances only) dissolved in the soil solution. Their movement may be enhanced by water movement through irrigation or rainfall. If in granular formulations, their distribution may be enhanced by physical incorporation into the soil.
Side Effects of Nematicides
- Groundwater contamination with toxins
- Exposure to chemicals
- People who use machinery for insecticide application are at higher risk.
- Delayed harvest
- Specific minimum time for residual effect to fade away is required which may postpone harvest.
- Pesticide poisoning
- HIgher levels of mortality occur when certain regulations for usage are not followed.
Rodenticides

Rodenticides are chemical pesticides, designed specifically for the extermination of rodents such as rats and mice.
Most rodenticides are lethal and do not serve only as repellents. They are produced and applied in the form of food which the rodents consume. It may take several hours to a few days for a rodent to be killed after consuming a rodenticide.
However, rodents often sense the threat and observe the rodenticide for a long time before consuming it. This is known as poison shyness and to reduce this, scientists now develop rodenticides with a very strong residual effect.
Instead of killing the rodent instantly, it causes dehydration and haemorrhage which cannot be stopped. This helps for avoiding problems related to rodents dying inside tiny crevices.
Are rodenticides dangerous to my pet?
Generally, rodenticides are considered to be a threat if consumed by other animals but that is a serious concern only if huge amounts of the chemical pesticide is consumed.
Secondary poisoning may occur if a rodent that has died from poisoning is consumed by a pet such as a cat. This only happens when an anticoagulant rodent bait has been used for the rodent infestation.
Such anticoagulants have a residual effect and the poison is stored inside the livers of mice and rats. When a predator eats the dead rodent, the poison from the liver gets spread inside the system of the other animal and second poisoning is observed.
However, this should not be a concern since modern rodenticides require multiple cases of consumption until they have a deadly effect. This is why you should always place more rodent poison whenever you see that the initially applied has been consumed.
Common Rodenticides
Anticoagulants
As mentioned above, an anticoagulant is the type of rodenticides that may cause injury or death to another animal after a secondary poisoning.
When consumed by rodents, anticoagulant requires one or two weeks to exterminate the rodent. The number of ingestions required depends on the generation of the anticoagulant insecticide. If they are from the first generation, multiple doses are required. In case they are a 2nd gen even a single-dose is enough to put an end to almost any rodent with a moderate size.
Anticoagulants cause death to rodents because they block the vitamin K cycle which causes a malfunction in the blood-clotting process.
A list of anticoagulants – rodenticides
- Warfarin
- Chlorphacinone
- Diphacinone
- Bromadiolone
- Difethialone
- Brodifacoum
- Bromethalin
- Cholecalciferol
- Zinc phosphide
- Strychnine
Metal phosphides
Metal phosphides are rodenticides that kill vermin with a single dose. They are fast-acting and death from ingestion occurs in 1 to 3 days. Of all metal phosphides, zinc is the most popular for rodenticide usage, mixed with food.
If other types of rodenticides have been used before without good success, it’s recommended to switch into a metal phosphide rodenticide. This is required because rats and mice give offspring too frequently and adapt to a pesticide within a short period of time, after which it has no effect on them.
A concentrate of about 0.75% to 2.0% is usually is added in rodenticides of this type. Such poison baits are distinct because of their strong garlic flavour. The odour is in fact very attractive to rodents but repels other animals which makes it very versatile as other animal species will leave it aside instead of eating it, which may disrupt the rodent extermination process.
Secondary poisoning, when metal phosphides are used, is not an issue. The risk is very low to zero because phosphides cannot accumulate in the liver of an animal similar to anticoagulants.
Hypercalcemia-causing Pesticides
Those are chemicals such as Calciferols, cholecalciferol and ergocalciferol. For people, these are healthy vitamins but to the rodent, they affect negatively the homeostasis in the body. When the rodent eat enough poisonous baits which cause hypercalcemia, the calcium levels increase so much that it starts to dissolve in the blood plasma.
The organs of the rodent that get most damaged are kidneys, stomach and lungs – the literally harden and become calcified.
Such rodenticides may not be deadly for your pet after an accidental consumption but its health may be affected. Always place poisonous baits in crevices where animals different from the targeted pest for extermination won’t be able to gain access.
Additional Less familiar Rodenticides
- Barium carbonate
- Chloralose
- Endrin
- Fluoroacetamide
- Phosacetim
- Pyrinuron
- Scilliroside
- Sodium fluoroacetate
- Strychnine
- Tetramethylenedisulfotetramine
- Thallium sulfate
- Nitrophenols
Advantages and Disadvantages of Chemical Pest Control

Chemical pest control is used across the whole world although it’s a double-edged blade. It provides decent efficiency in most cases but at high costs in terms of ecological impact. However, in many cases, it appears to be the only reasonable solution. For this reason, you should take a look at the two different point of views – chemical pest control with its advantages and why it’s not such a good practice for pest extermination.
Advantages of Chemical Pest Control
- Effectiveness
Chemicals exterminate any pest that hasn’t adapted to the deadly substance inside the agent. They eradicate fast and with an efficiency of up to 100%. Most are very easy to apply and can get in the way of pests that hide in small crevices and other hidings. - Quickness
Some chemicals for pest control kill slowly because of the active ingredient. However, most pesticides are designed to exterminate the vermin in less than 3-4 days, which is much faster compared to organic methods of pest control such as importation or augmentation. - Precise targeting (localized)
Contrary to biological pest control methods, the chemical substances may target a specific area with high precision. On the other hand, if you release pest-destroying animals, there is no control over their behaviour – they may spread wherever they want. - Easy application
This one helps the customers a lot in their efforts towards DIY pest control with ready-to-use products. Most pesticides sold on the market are packed inside bottles, designed for easy use and application. They are readily available and spraying them on your crops takes few minutes and a little more time before that to read the instructions, which is something we highly recommend before using pesticides of any type. - Improving productivity
Pesticides become more and more effective in time but sometimes at the cost of being more toxic and unsustainable. Efforts of scientists are made towards researching pesticides that cause lower pollution and side effects on human health. However, it’s difficult to achieve that because animal species evolve against the chemicals and more poison is required to exterminate pests that are resistant to the old forms of pesticides. - Sports facilities maintenance
Sports facilities such as pitches and football terrains are endangered by pests too. If the turf is not maintained properly, it will be destroyed and the field will become unusable. Pesticides are used even there for the exterminate pests such as white grub worms, chinch bugs, bluegrass weevils, ants and more.
Disadvantages of Chemical Pest Control
- Promote evolution
We already mentioned this but it’s never useless to explain it further. The use of chemical pesticides stimulates the pest to develop resistance to the chemicals used in the pesticides. The resistance is based on alterations in the genetics of the vermin and every future generation becomes increasingly pesticide-proofed. This works very well among rodents which produce several litters per year. - Resurgence (non-precise targeting)
Resurgence happens when the use of pesticides affects the environment and disrupt the organic pest control. The most tremendous side effects of all are when significant animal species such as bees get killed by collateral damage after spraying with chemical pesticides.
Another side effect of resurgence is when pest-destroying animals such as parasitoid wasps are killed and they pray, mostly other pest insects, no longer have a natural enemy and start to multiply so quickly that completely overwhelm entire agriculture. - Persistent Organic Pollutants
POP, known as persistent organic pollutants, are extremely dangerous to the non-target organism but also affect the health of people by causing cancer, infertility or problems to the endocrine system.
Impact of Chemical Pesticides on the Environment
- Surface water contamination
- Ground water contamination
- Soil contamination
- Air contamination
- Effects on plants
- Effects on animals
- Direct impact on humans
Texture of Chemical Pesticides
There are chemical pesticides in different form. You can find it in liquid or harder form and each has its specifications, advantages and disadvantages. These are the most common forms of chemical pesticides.
Granules / pellets

The insecticides are soaked into coarse particles such as ground corn or nut shells. This way the toxic chemicals come out slowly and have a residual effect. The environment is polluted not at once but instead much slower.
Such type of insecticides is used against soil-dwelling insects for more effective results and penetration into the soil.
Dusts chemical pesticides
Inert particles such as ash, chalk and talk are used for making a pesticide in dust form. Their most comprehensive application is to disperse them directly onto the surface. Such a particle is usually so small and thin that they immediately stick to the body parts of insects.
This makes it easier for the active chemical ingredient to start taking effect right after the moment of application. Dust chemical pesticides are very unsuitable for application in the open as they are very easily spread by the wind and get into the human body through the respiratory system.
Soluble powders / Wettable powders
Those are chemical pesticides which are distributed in a powder-like form and require to mix them with water. Such foliar insecticides are described as wettable powders due to the ease of their transportation.
Emulsifiable concentrates
Chemical pesticides based on emulsifiable concentrates do not have a residual effect on fruits and vegetable. They are mostly used in the form of sprays to treat pests in urban and industrial areas.
In standard emulsifiable pesticides, the emulsifier is usually dissolved in an organic solvent and the chemical concentration is watered with higher amounts of water.
Aerosols
Those are insecticides that have been produced and packed inside a spray can and have a solvent inside, added by the manufacturer. Such pesticides have a very long expiration date and are in most cases ready-to-use immediately after purchase.
Some aerosols are designed specifically for fogging machines that are used by pest control experts for fumigation services indoors and outdoors.

Panther Pest Control Blog
Keep your home pest-free with Panther Pest Control:
- Expert pest control services for homes and businesses.
- Safe, effective, and environmentally-friendly treatments.
- Trusted professionals dedicated to eliminating pests for good.
The history of bed bugs in the UK begins a little while before WWII. The Cimex lectularius is the type of bed bug that is native to Europe and the UK. Bed bugs weren’t common to the UK until the 1930s and since then the problem has grown.
In fact, immediately after WWII, it’s reported that nearly 30% of British homes were infested with these wicked bugs. Such a drastic increase in their population was attributed to the heating systems used in homes which created more pleasant living conditions for them to thrive in.
In 2017, The Sun published an article saying that “…the numbers of bed bugs have tripled in the past five years.”
This is not only a problem because it sounds like an almost epidemic level of bed bugs in the country, but also because over time bed bugs have become resistant to many of the pesticides once used to eradicate them in all of their life stages.
Where do bed bugs come from?
The origin of bed bugs dates back hundreds of years BC, back when our ancestors lived in caves. The bugs originally were parasites that used bats for hosts and lived with them inside caves. Then people came into the caves and they turned into another fantastic host for the bugs to feed on. With time, people came out of the cave, moved to other continents and bed bugs hitchhiked and moved too. They spread through Europe and Asia, and then to the rest of the continents.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WfKCcSPCOQo&t=17s
But where do they come from when they infest your home is another matter:
- If you live in a block of flats, this increases your chances of getting them in your home if one flat has them already. They can travel from flat to flat.
- Another way they can turn up in your home is if they are brought inside. A friend or a family member can bring them if they were in an infested place before that. Bed bugs will hitchhike on clothes, bags, shoes. The worst thing is that even one female bug can create an entire infestation in your house.
- Bed bugs can also be brought into your home after your vacation or work trip. If you stay in an infested hotel room, you are almost 100% guaranteed to bring them back home.
- They can also enter your home with the purchase of second-hand furniture. Bed bugs don’t only live on beds or near them. They can live in other pieces of furniture that people spend a lot of time on. Be extremely careful if you are buying used furniture.
- Used clothes can also have bed bugs on them. And even new clothes can have them. If a person who has an infestation has tried something on and you buy it, even one bed bug can be on it and then lay eggs in your home.
What attracts bed bugs? To you? To your home?
- They are parasites that feed on human blood, so it’s the main thing that attracts them.
- They also sense your body temperature and the carbon dioxide that you breath out, and that’s how they find you at night. They use these things as orientation for where you are, they crawl on your bed and find the best place on your body to feed.
- Hiding places. They will need to hide somewhere near your bed or other furniture where you spent time on. Cracks in walls, even power outlets will do, skirting board, bed frame, carpet near the bed, etc. Professional pest exterminators would advise you on keeping clutter to minimum.
Signs of bed bugs
- Black spots on your mattress or sheets – it’s bed bugs’ faecal matter. It’s gross, yes. And if see some black dots, it’s probably them.
- Red spots on the sheets – this would be your own blood. After they’ve fed and left you alone, some tiny drops of your blood may have dropped onto your sheets.
- Itchy hives – which are bed bug bites. In 24 hours period after the initial biting, you may see red hives on your body. Try not to scratch them and risk getting it infected. If the area gets infected see your doctor, bed bug bites are a serious matter.
- Skins and eggshells – Dead skins or empty shells are a sign of a growing infestation.
- Eggs or live bugs – Even though they only grow up to 5mm in length, you can see the bugs with a naked eye. If you see a reddish-brown tiny bug on your bed or near it – it’s a bed bug.
Do bed bugs jump?
No. They don’t jump, they don’t fly. They just walk and climb. They’ve never been able to jump or fly and let’s hope they never are.
Where do bed bugs live?
Highly populated areas are also highly populated with bed bugs. They are considered a common pest in the UK in the latest years because the number of people travelling internationally has increased. Bed bugs thrive in Spring, Summer and early Autumn. Your London home provides great living conditions for them because of the typical UK weather and temperatures. They prefer dark places so you won’t see them out in the open in the daytime.
That’s why the places in your home where bed bugs live are:
- Your mattress
- The box spring of your bed
- Walls near your bed or other furniture
- Night stands near your bed
- Baseboard or bed frame
- Closet and clothing
- Sheets
- Curtains and carpets
- Sofas, armchairs or other furniture where you spend time
How long do bed bugs live?
Bed bugs live comparatively longer than most types of insects. Since hatching, the life of a bug can go up to one year under perfect conditions. If not, it can live for up to ten months in general.
How long can a bed bug live without feeding? An adult bug can live without feeding on a host anywhere between two weeks and over a year, иf it lives in a place with the right amount of humidity and temperature.
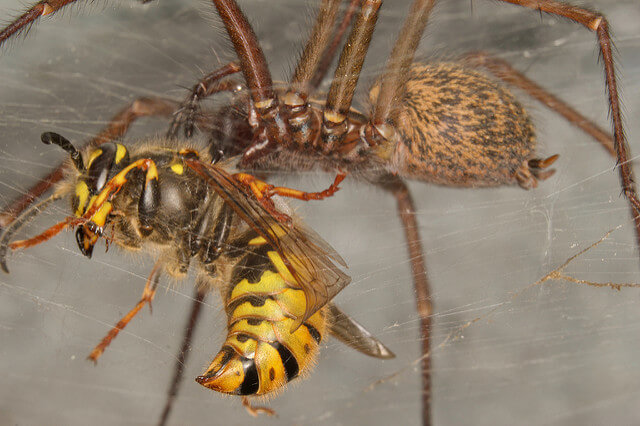
Do spiders eat bed bugs?
Yes. Spiders eat bed bugs. There is usually more than one type of spider in every UK home and spiders feed primarily on other insects.
Other enemies of the parasite bugs are cockroaches and centipedes. Both of which are also a common household pest in the UK and would also eat bed bugs. But you shouldn’t rely on another type of insect to help you win the battle with pests.
How to kill bed bugs?
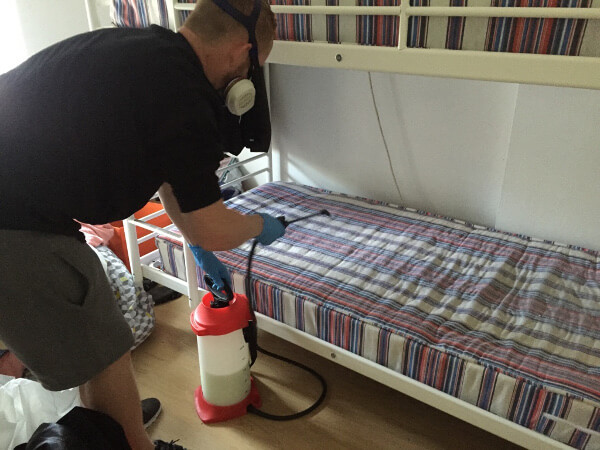
This is a complicated problem, like you on your own are unlikely to manage to clear the infestation. Bed bugs can die at very high or very low temperatures, or they are treated by an insecticide with industrial strength. DIY bed bug treatments often end badly, so be careful. If you suspect an active infestation book a professional bed bug treatment to save your home.

Panther Pest Control Blog
Keep your home pest-free with Panther Pest Control:
- Expert pest control services for homes and businesses.
- Safe, effective, and environmentally-friendly treatments.
- Trusted professionals dedicated to eliminating pests for good.
There is a huge interest among people about the difference between a queen wasp and a normal wasp. From Panther Pest Control we decided to make a detailed post about it that contains the most common questions related to this interesting topic.
In this guide, you will learn how normal wasps turn into queens, how the two types of wasp live, hunt and multiply.
How Does a Wasp Become a Queen Wasp at First Place?
To get a queen in a wasp nest you need fertilized eggs. These eggs contain female wasps which are usually the workers in the colony. There is always at least 1 queen in the nest, which choose the females wasps that will be turned into the new queens.
When the choice is made the queen wasps start a complex process of special care for these wasps. It’s still somehow unknown the process of turning specific normal wasps into queens. Scientists say there is a special hormone which the queen gives to the choselogn wasps. Afterwards, these insects that have been given special care, grow faster and differently, finally turning into the new queens of the colony.
How Big is a Queen Wasp – Difference in Queen Wasp Size
Usually, the queen wasps resemble the workers at almost 100% and are very hard to identify it. Is some wasp species like yellow jackets, the queen is longer than the workers and can be easily noticed.
The difference in the queen wasp size is about 0.64cm and similar diversity in the size may be observed in other insect species such as ants and honeybees.
The lower abdomen of the queen wasp is pointed in contrast to the normal wasp. All insects of this kind are omnivorous and reach a maximum length of about 2.5 – 3.8cm
Queen Wasp Identification
To distinguish the queen wasp from the worker wasps can be a challenge. Normally there aren’t big differences for most wasp species. With some, however, the queen is a bit longer. And for some species, the queens also have a pointed lower abdomen and a narrower waist. But for example, with paper wasps, there is absolutely no difference in the size so you’ll never know which one is the queen.
Since the queens are the only wasps that hibernate in winter, you should know that if you see a solitary wasp in late autumn or early spring, it is most likely the queen
Where Do Queen Wasps Hibernate?

Wasp queens look for narrow places under a shelter where they can get into during the winter. The place should protect them mostly from temperatures but from humidity and predators as well. Crevices and holes into the walls of the building provide good shelter.
No matter how well they hide, almost all wasp queens that have been produced in the nest die during the winter as they become victims of other animals, mostly arachnids like spiders who hide in the same places where the queens hibernate.
Another major threat for the hibernating queens is warm winters. When wasps wake up too early, there is no food for them and starvation wipes them out in a short time.
Hornets may be a terrible disaster when they wake up too early, especially if they are Asian hornets.
Where Normal Wasps Hibernate?
The majority of the wasp colony does not hibernate. Normal wasps get wiped out during the winter because of starvation caused by lack of food. The queens that are sexually mature are the only wasps that go through a successful hibernation process if the temperatures are low enough until the end of the winter.
When do Queen Wasps Come Out of Hibernation?
There is a lot of interest on questions like “when queen does the queen wasp leave the nest” so I decided to sum it up quickly.
The new year for the wasps starts when the winter ends, and the spring comes. During the first days of the spring, the warmer temperatures wake up the queens and break their hibernation process.
The next thing that needs to be done depends entirely on the queens as there are no other wasps alive at that time of the season. The wasp queens have to find a place which is very convenient for a nest. Then they start to gather materials of which the nest will be made. Wasps often make nest in lofts, which may prevent them from going through hibernation if it’s too worm inside the structure.
What Do Queen Wasps Eat?

What Normal Wasps Eat?
The diet if the normal wasps is quite different, only adult workers are eager to use flower nectar in the late spring, the rest of the wasps in the nest will not take part in pollination at all. Most of the the time, adult wasps spend on searching for food for their young.
These food-seeking wasps kill other insects and small arachnids like spiders and feed the smaller members of the colony on their victims, thus ensuring the survival of their species.
Some wasp species are omnivorous and also feed on fallen fruit and dead insects. Adult male wasps very rarely fly to flowers for nectar, usually when there is no other food source available around.
How Queen Wasps Build Wasp Nests?

The process of building a wasp nest starts immediately after the winter ends and the queens get out of hibernation.
- Scavenging materials
- Once they find the perfect place for the nest, the wasp queens start to gather the material they need to build it.What works best is mix of wax, saliva and chewed fabric (wood or synthetic material). It all begins with finding something that is stable and firm to which the nest will be attached, quite often this is the place under the roof of a house and inside sheds, bird boxes, garages and cavities.
- Laying eggs
Once the wasp nest is ready, the queens lay their eggs there and start searching for food to ensure sustenance for their larvae. The food for the larvae should be rich in protein as this increases the speed of their growth and leads to a healthy colony.
What normal wasps do about the nest?
- Hunting
Normal wasps make an important contribution to the wasp nest as well. Most of the time they hunt insects and search for other type of food. Each group of wasp species has to care for the offspring and do whatever it is required to ensure their survival.There are also wasp species known as beewolf wasps. These are very harmful for the environment because their favorite prey are honey bees, which on the other hand are very important because of the pollination. Adult beewolf wasps feed on pollen and nectar which is practically, stealing the food of the bee species. - Stealing and infiltrating
Some wasp species steal the food of other wasps and even lay eggs in the nests of wasps from a different colony. Specific types of solitary wasp species build special types of wasp nests in which each insect has a private cell. It lays eggs there and brings immobilized food to the larvae. Then seals the exit and leaves the larvae with the food inside which they later use as a source of protein to finish they life stages.
Queen Wasp Sting. Is it More Dangerous?

The queen wasp is not more dangerous than the sting of a normal wasp, although the anatomy of the queen wasp sting is a bit different, mostly by its size as the insects are a bit bigger.
Wasps, bees and hornets sting either in self-defence or when their queen is threatened. You might get attacked if you get too close to their nest but such unfortunate events are less possible, but not impossible.
In this picture of a queen wasp sting, made with a microscope in 1913, you can see the anatomy of the sting. There are two small barbs in the tip and each has a very specific and important purpose.
The first one is supposed to stabilize the victim so that the second barb can go in easily and with precision. Once the victim is immobilized by the first barb the second one injects the venom that paralyzes the stung victim completely, usually, these are other smaller insects, bees and more.
Does Killing The Queen Wasp Get Rid Of The Nest?
Killing the queen was can help you but it must be done at the right time. The queen must be killed before the nest is built and the eggs are already laid. The queen starts building a nest in late spring, so around that time, you can try killing it. You can also kill in during the winter if you find it hibernating near your home. Preventing the nest’s completion is the best choice to saving your home from a wasp nest.
Wasp Extermination and Wasp Nest Treatment
If you need any help with any form of wasp control whether it is a wasp nest treatment or complete wasp extermination, we would love to help you with it. Call us 24/7, give us detailed information about your wasp infestation and get a precise quote for the service.